Do you need to cut stone, ceramics, or concrete? Every material has different properties, and the composition parameters of a diamond cutting blade segment are set according to those properties. In the following lines, we will mention all the options you may encounter when choosing a diamond blade.
Table of Contents
- Classification of diamond cutting blades by material type
- Classification of diamond cutting blades by segment shape
- Types of diamond cutting blade mounting
- What are the advantages of flange cutting blades?
- Dry or wet cutting? Classification of diamond blades by method of use
- What blade diameter is suitable for your work?
- Special blade sizes found only with true specialists
- Classification of diamond blades by direction of use
- Types of diamond cutting segments
Classification of diamond cutting blades by material type
- Concrete cutting blades are suitable for cutting building materials such as concrete blocks or paving, as well as large-format cutting of reinforced concrete panels.
- Asphalt cutting blades have a diamond segment more resistant to abrasive materials and, at the same time, durable enough for potential cutting of reinforcement bars.
- Ceramic cutting blades, glass, and porcelain have a segment design adapted for precise cuts that are gentle on the glaze. They are characterized by a thin and sharp cut.
- Stone cutting blades are a specific group. This includes blades for natural stone (granite, marble, sandstone, ...) or artificial stone (engineered stone, conglomerate, ...).
Classification of diamond cutting blades by segment shape
- Segmented blades are tools with a classic design featuring separate teeth, most commonly used for cutting concrete and stone. This design is suitable for optimal cooling.
- Continuous blades, also referred to as RIM blades, are used for cutting materials where a clean cut without defects or chipping is required—primarily ceramics and tiling materials.
- TURBO blades are specific for their interleaved segment, which offers optimal cooling and dust removal from the cut. They are used for cutting granite and concrete.
- Surface-applied diamond blades, EP (electroplated) or VB (vacuum brazed), are used for processing marble or ceramics.
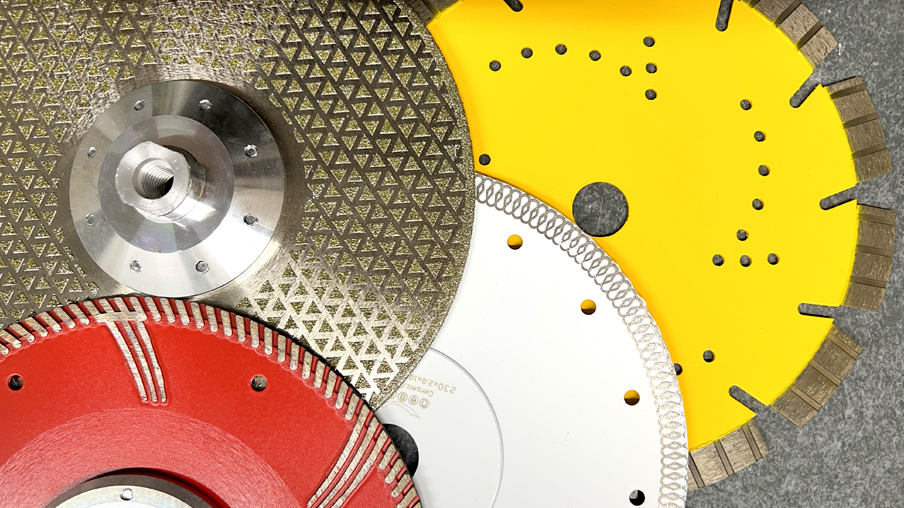

Various types of diamond cutting segments suitable for reinforced concrete, ceramics, marble, or granite.
Types of diamond cutting blade mounting
In our offer, you will find cutting blades from minimal dimensions suitable for hand-held angle or straight grinders up to large saw blades used in quarries. Every cutting blade has its own mounting hole for the machine. If your chosen blade has a larger hole than you need, you can use a reduction ring.
- 6 mm Shank or 3 mm - for direct sculpting grinders.
- Flange 22.23 or M14 - its advantages are mentioned in the article below.
- 22.23 mm Bore - the most common way to mount a tool in an angle grinder.
- 25.4 mm Bore - the most preferred diameter for road, hand-held, and table saws.
- 27 mm Bore - a less preferred mounting size.
- 50, 60, 90, or 100 mm Bore - shaft diameter used in large bridge saws for cutting stone.
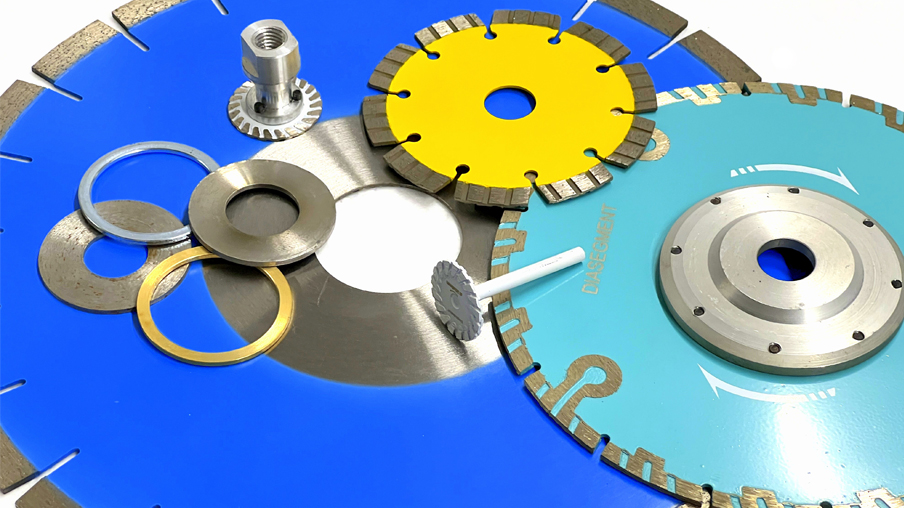

Detail on various mounting methods for diamond cutting blades.
What are the advantages of flange cutting blades?
Cutting blades with an offset are also called "undercutters." Since no locking nut is used, the shaft thread does not protrude on the bottom side where the diamond blade is mounted. This creates a flat plane on the underside, allowing for more possibilities when working with the tool. For example, using a grinding-cutting blade, you can cut or grind directly across the surface, similar to a grinding cup.
Flange blades are very popular not only for masonry or sculpture work but also for cutting openings in ceramics with a 90° angle or when undercutting panels directly at the floor level.
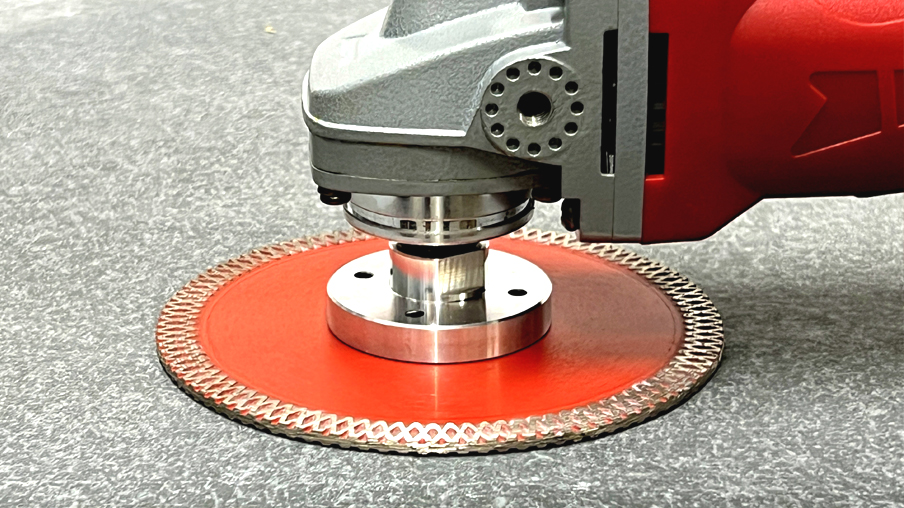
The advantage of a flanged grinding-cutting blade is the possibility of surface processing of the material, similar to grinding discs.
Dry or wet cutting? Classification of diamond blades by method of use
Working with a diamond blade involves relatively high temperatures that can cause permanent damage. Therefore, it is important to cool the diamond segment appropriately.
- Cutting blade intended for dry cutting - the diamond segment of the cutting blade can withstand higher temperatures generated during dry work. It is important to adjust the working technique with an emphasis on regular cooling.
- Cutting blade intended for wet cutting - water is essentially a lubricating and cooling medium that also effectively removes excess sludge from the cut. Tools designed for wet work provide a cleaner cut with a nice edge and offer higher durability and economic efficiency.
What blade diameter is suitable for your work?
The choice of tool diameter primarily depends on the machinery you have. As mentioned in the article, it is dangerous to use a different, especially larger, diameter than recommended by the machine manufacturer. Another factor is the depth of cut you need to perform. In such cases, the cutting depth can be calculated from the blade diameter. However, don't forget to take into account the size of the machine head from which the mounting shaft emerges.
- Diameters from 20 mm to 230 mm are most commonly used in hand-held angle grinders. Working with a cutting blade larger than 230 mm in a hand tool is truly only for experienced masters.
- Blades with a diameter of 250 to 350 mm are used in small table saws, for example, for cutting tiling materials.
- Diamond cutting blades from 300 mm diameter are used in larger machines such as road saws, large hand-held saws, or bridge saws.
In general, the most preferred diamond cutting blade diameter is 125 mm. Working with this diameter is not too physically demanding, making it suitable for sensitive or detailed work in sculpture or tiling. We can say that the smaller the tool diameter, the easier the maneuverability, and conversely, a larger diameter holds the direction or plane better.
Special blade sizes found only with true specialists
In our range, you will find, in addition to the most common sizes, truly rare diamond cutting blade diameters. These are the smallest blades in sizes of 40, 50, 75, or 90 mm. Truly special diameters include, for example, 140, 170, or 190 mm. These are used in special hand tools for processing stone or building materials. And the largest of the large stonemasons buy diamond cutting blades with a diameter of 1000 mm from us.

Extremely popular flange blades for processing natural stone, concrete, ceramics...
Classification of diamond blades by direction of use
Cutting blade intended for straight cuts - ARIX, TURBO, or RIM type segments are thinner with an emphasis on a nice cut or performance. They are not suitable for shaping or grinding. There is a risk of tool damage and danger of serious injury!
Combined grinding-cutting blades - these are mostly offered with a flange that ensures more effective use of the grinding surface. They are suitable for stonemasonry and construction work.
Convex shaping blades - the dish-shaped body of the cutting blade is designed for cutting and grinding spherical surfaces. It is used in sculpture work, but also for shaped cutouts, such as for a sink in a stone slab.
Types of diamond cutting segments
Sintered diamond segment - classic design as you know it with most standard diamond cutting blades.
Turbo segment - the interleaved diamond segment ranks among high-performance tools primarily intended for professional use.
RIM segment - continuous segment without gaps is used for tools intended for cutting ceramics, glass, or tiling materials.
ARIX segment - with technology involving diamonds arranged in rows, it is the absolute technological peak among diamond cutting tools. But ATTENTION! Not only the diamond arrangement but also the metal mixture—the bond in which the diamond is embedded—is extremely important for the overall result and tool quality.
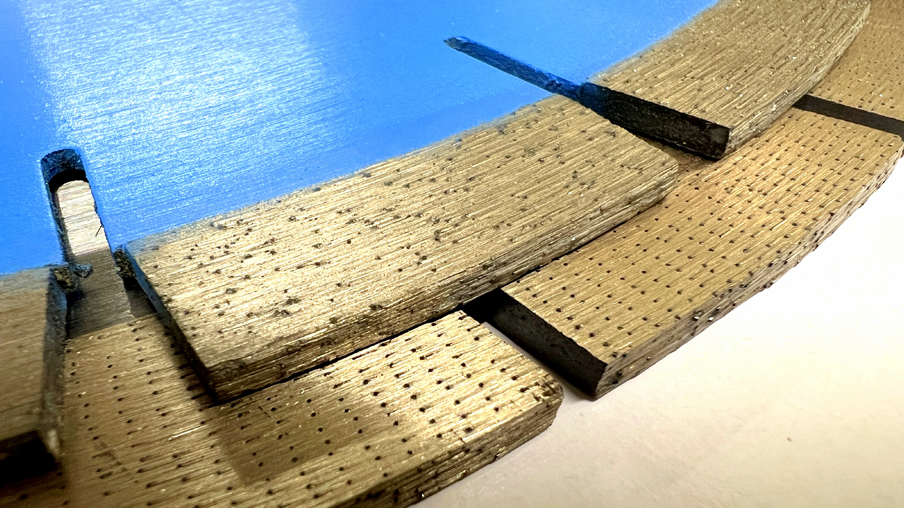
Detail on a classic cutting segment with randomly placed diamonds and ARIX technology with precisely placed diamond grains
Conclusion
As you can see, the offer of diamond cutting blades is truly diverse. From our own experience, we know that there is a higher probability of using the wrong type of tool than the possibility of the tool being of poor quality. Therefore, we recommend consulting your choice primarily with an experienced dealer, not just a salesperson.

Pavol Šáray
CEO & Technical Expert DiaSegment
I spend most of my time in the field with customers, where we look for the best solutions for their specific tasks directly at construction sites or in stonemasonry workshops. These trips are my greatest inspiration – I then process practical insights into technical articles to help you navigate the subject. Since I am often fully engaged in work, you may not reach me immediately, but I will be happy to devote full attention to your questions.
✉️ E-mail: diamantovenastroje.cz@gmail.com
📞 Mobile: +421 903 528 039
Available on business days 8:00 – 16:00.
If I don't answer, please send me an SMS or WhatsApp, and I will get back to you.
